ACE1049:
GLOBAL CONTROVERSIES,
CRISES & CITIZENSHIP:
ISSUES AND SOURCES
TARGET: Stage 1 students on
the ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCE, AGRI-BUSINESS MANAGEMENT and COUNTRYSIDE
MANAGEMENT degrees.
AIMS:
1. To encourage students to become familiar with current issues and controversies in
agriculture, food & rural development globally.
2. To understand basic data interpretation and synthesis.
3. To practice analysing
and presenting data and argument/stories.
4. To provide students with basic information literacy and information
technology training.
5. To understand how
data and knowledge is used in academia, public policy, business and
practice.
6. To develop communication
and study skills to enable independent learning at a HE level.
THE ISSUES:
- The world is pretty full
- see also CEISIN
- SEDAC: Socio-economic Data and Applications Centre, or The Population Reference Bureau.
There is
virtually no 'new territory' for expansion -
No more scope for such major migrations as happened between 1850 and
1914, when a million people a year emigrated to the new world
from Europe. See here for the 'social
mechanics'
of population growth. and a sociological
historial perspective. (QUESTION - who produced
these pages, and what provenance are they likely to have?).
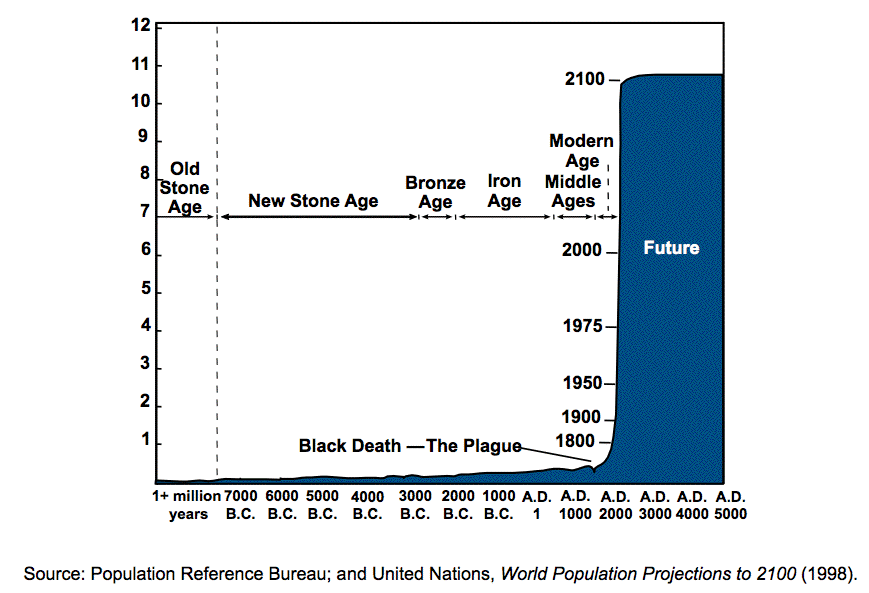
What is wrong with
this picture?
-
There is no away to throw to - we run the risk of being
buried or drowning in our own refuse, and of seriously
altering our climate (probably for the worse).
-
Natural Resources are finite - as
we consume more non-renewable resources (oil, coal, gas and minerals)
so further use will become more expensive, or see here or here or here
for more
of the debate - though can we 'validate' any of these sites?
-
Technology is different, more capable and
quicker - so mistakes are (perhaps) more likely and
bigger, and villainy has more scope.
- But, we should all be
smarter - learning from history and standing on the shoulders of giants
- the future is up to you!
SOME BACKGROUND:
As an introduction to the recent
history and current state of the world, try GAPMINDER
WORLD - an excellent visualisation of our current condition, or try
WORLD
MAPPER - for a different perspective.
YOUR TASKS:
- IDENTIFY, DESCRIBE, RATIONALISE AND
PROVIDE SOURCES FOR A SPECIFIC FOOD SECURITY ISSUE,
FROM YOUR PERSPECTIVE.
- OUTLINE THIS ISSUE - AND ITS KEY/CRITICAL
DIMENSIONS - IN A POSTER
- DOCUMENT YOUR EXPLANATION AND ANALYSIS OF
THIS ISSUE WITH YOUR
'INDIVIDUAL SEARCH STRATEGY
AND ANNOTATED BIBLIOGRAPHY' AND YOUR
INDIVIDUAL LEARNING LOGS
FOOD SECURITY:
"Continuing population and
consumption growth will mean that the global demand for food will
increase for at least another 40 years.
Growing competition for land, water, and energy, in addition to the
overexploitation of fisheries, will affect our ability to produce food,
as will the urgent requirement to reduce the impact of the food system
on the environment.
The effects of climate change are a further threat.
But the world can produce more food and can ensure that it is used more
efficiently and equitably.
A multifaceted and linked global strategy is needed to ensure
sustainable and equitable food security." Source - Godfray et
al, Science, 2010
WFP World Hunger Map
IFPRI World Hunger
Index
The UK's Global Food Security Programme. (see, especially, "the issue")
Definition? The UN World Food Summit, 1996, defined food security as
existing “when
all people at all times have access to sufficient, safe, nutritious
food to maintain a healthy and active life”. - see, e.g. the UN
WHO site for elaboration.
Since 1960, the world's population has grown from 3 bn. to 7 bn
(October, 2011) - the suprise, perhaps, is not that there are still so
many hungry in the world, but that there are so (relatively) few.
The major reason is the "Green
Revolution"
We now need at least a Doubly Green
Revolution (Gordon Conway, 1998 - and his new book (2012, with Kate Wilson) "One Billion Hungry: Can we feed the world?"
Need to produce enough food for
9bn. people by 2050,
without destroying much (or any?) more of the natural environment,
without using as much fossil fuel energy (rather than more),
using less (or no more) water,
in the face of a less reliable, and possibly less benign climate.
A Quadruple Green Revolution
- and it is all up to you.
Some indicative issues.
Don't forget the history: see, e.g. Fuglie & Wang, 2012 (Amber Waves)
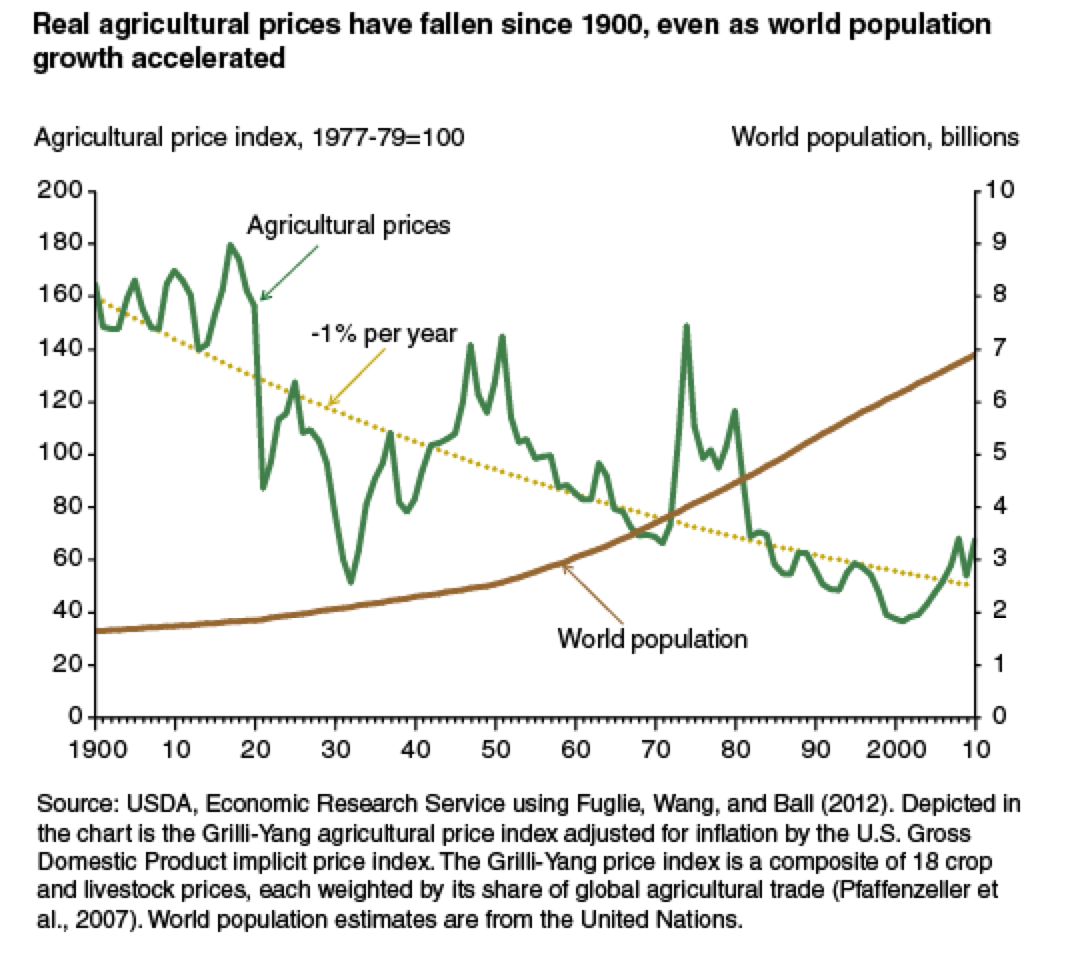
Some
Recent References on the issue of global food security
[Note - Godfray et al, Science,
2010, is an important and relatively recent source.]
'Food
security: feeding the world in 2050' Special issue of the
Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, September 27, 2010;
365 (1554), compiled and edited by H. Charles J. Godfray, John R.
Beddington, Ian R. Crute, Lawrence Haddad, David Lawrence, James F.
Muir, Jules Pretty, Sherman Robinson and Camilla Toulmin (which reports
the findings of the UK Government's Foresight
Project on Global Food and Farming Futures (report published,
January 2011)
Ana Iglesias,
Sonia Quiroga and
Agustin Diz: "Looking into the future of agriculture in a
changing
climate", European Review
of Agricultural Economics, 38 (3), August,
2011 p 427 - 447,
for
a recent
summary of work under the EU CIRCE Project and related work on
Agriculture and Climate change.
Alex Evans, "The
Feeding of the Nine Billion: Global Food Security for the 21st Century",
Chatham House Report, January 2009
Nelson, Rosengrant, et al.
"Climate
Change: Impact on Agriculture and Costs of Adaptation". Food Policy
Report. International Food Policy Research Institute, Washington
DC: USA. 30 p.
Nelson, Rosengrant et al. "Food
security, farming, and climate change to 2050, Scenarios, results,
policy options", IFPRI Research Monograph, 2010, and related
Policy Brief: "Food
security and climate change: Challenges to 2050 and beyond"
Martin
Parry, Alex Evans, Mark W. Rosegrant and Tim Wheeler, "Climate change and hunger:
Responding to the challenge", World Food Programme, 2009
Foley et al, 2011, Solutions
for a cultivated planet, Nature,
478, 337–342, October, doi:10.1038/nature10452,
[what, exactly, is the analytical framework here? e.g. See if you
can discover how they estimate the size of their 'yield gap', and thus
the consequences of closing it] - see, e.g. FAO, CFS, HLPE - "Price
Volatility and Food Security" - especially p. 34.
Swinnen, 2011: "The
Right Price of Food", Development
Policy Review, 29, 6, November, 667 - 688, which points
out and explains why international organisations and NGOs (Non
Governmental Organisations) such as Greenpeace and Oxfam 'bend' the
'truth', at least as far as headlines are concerned.
[And, in a similar vein, and from the same 'stable':
Vandemoortele, 2009, "The
MDG Conundrum: Meeting the Targets Without Missing the Point",
Development Policy Review, 27, 4,
November, 355 - 371]
Harvard Centre for International Development: "Enhancing
Food Security in an Era of Global Climate Change: An Executive
Session on Grand Challenges of the Sustainability Transition, San
Servolo Island, Venice – June 6-9, 2010",
[Who is doing and has done the major thinking and
research on global food security? - how reliable do you think
these
people are - more to the point, where might you look for alternative
research?]
A model?
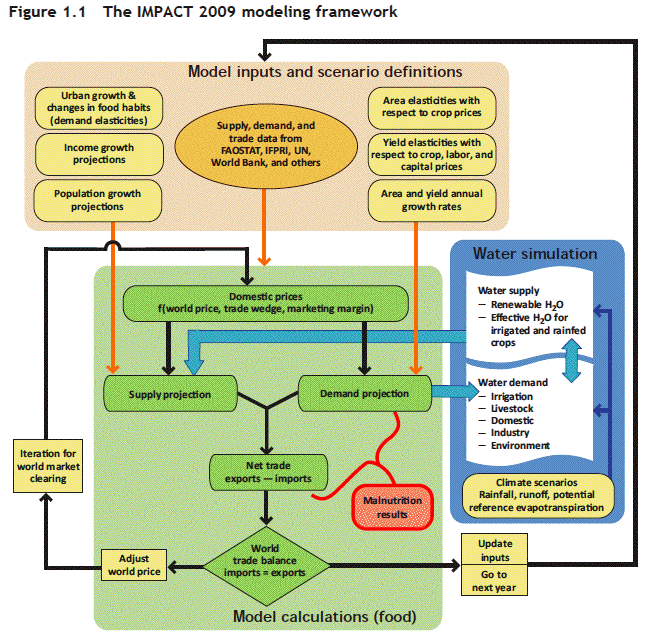
Source:
Nelson et al., 2010, p. 6. (can you spot the 'deliberate error'??)
MAJOR STATISTICAL SOURCES:
OECD/FAO Agricultural Outlook: 2012 - 2021.
United Nations World Food
Programme. See, e.g. World Hunger Map
(above)
World Bank:
a vast amount of data by country, including 420 indicators from the World
Development Indicators (WDI) covering 209 countries from 1960 to
2008, which can be displayed as tables, maps or graphs, under the
headings:
Agriculture & Rural Development; Infrastructure; Aid
Effectiveness; Labor & Social Protection; Economic Policy and
External Debt; Poverty; Education; Private Sector; Energy & Mining;
Public Sector; Environment; Science & Technology; Financial sector;
Social Development; Health; Urban Development.
WB's Annual World
Development Reports "Published annually since
1978,
the World Development Report has long been an influential publication
and an essential reference on the world economy and the state of
economic and social development. Each year's report focuses on a
specific topic in development such as labor, infrastructure, the role
of the state, transitional economies, health, the environment,
agriculture, or poverty."
World
Development Report, 2009: Reshaping Economic Geography :
World Development Report 2010:
Development and Climate Change.
World Development Report 2011: Conflict, Security & Development.
World Development Report 2012: Gender Equality & Development.
Note, also, IFC's
Doing Business
Economy Rankings, "Economies are ranked on their ease
of doing business, from 1 – 183. A high ranking on the ease of doing
business index means the regulatory environment is more conducive to
the starting and operation of a local firm. This index averages the
country's percentile rankings on 9 topics, made up of a variety of
indicators, giving equal weight to each topic. The rankings are from
the Doing Business 2011 report, covering the period June 2009 through
May 2010."
United
Nations Statistics Division (UNSD), (whose site notes that
20.10.2010 is World Statistics Day) has major collections of data on
economic, social and development conditions world-wide. Especially
important are the Millenium Development
Goals data ("This site presents the official data,
definitions, methodologies and sources for more than 60 indicators to
measure progress towards the Millennium Development Goals. You will
also find the official progress reports and documents produced by IAEG.
Links to related sites and documents and constantly updated news will
keep you up to date with the ongoing activities on MDG
monitoring."). This site also includes MDGInfo 2010 online,
which looks very promising though I have not had time to explore it.
See, also, UN Department of Economic and Social Affairs (DESA), Population
Division: World
Population
Prospects: 2009 revision.
See, also, the UN Human Development Reports and Human
Development Index (for what the HDI measures, see the Compsite
Indices page) and Interactive
map of migration data.
See, also, UNITED
NATIONS ENVIRONMENT PROGRAMME (UNEP) - and the related site: GRID ARENDAL,
"Environmental Knowledge for Change", for detailed maps, graphics and
data. "Established
in 1989 by the
Government of Norway as a Norwegian Foundation, our mission is to
communicate environmental information to policy-makers and facilitate
environmental decision-making for change." Especially informative are
the Global
Maps and Graphics. - e.g. World
Greenhouse Gas Emissions by sector, and by
country, and population
by income level.
United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change UNFCCC
(1994), under which a "Conference of the Parties (COP)" to the
UNFCCC is held annually. COP17 is being held in Durban, South Africa,
28th Nov. - 9th December 2011.
See,
also, an excellent interactive data source for a new Multidimensional
Poverty Index, developed by the Oxford Poverty and Human
Development Initiative (OPHI)
in conjunction with the UNDP.
FAO
(Food and Agriculture Organisation)
for comprehensive data
on food supply, food balance sheets, food security, resources (land and
water etc.). See, especially, FAO's Annual Hunger Report
(e.g. recent media report on 2011 Hunger
report),
and their State of Food
Insecurity Report from the Food Insecurity and Vulnerability
Information and Mapping Systems (FIVIMS) site, and also their Special Programme
for Food Security (SPFS), and also their Committee on World Food Security
(CFS) and the associated "High Level Panel of Experts" (HLPE)
who have just published a report on "Price
Volatility and Food Security" (available on the HLPE site - link
above).
International
Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI) (part of the CGIAR
network) for major international food issues and data, including the 2011
Global Hunger Index (above). See, especially, IFPRI's
IMPACT
project: Food
security, farming, and climate change to 2050, which includes a
data visualisation tool for Food Security case maps, and also the Food
Security Portal (hosted by IFPRI)
IMF -
Global economic data, including commodity price indices, and a
visualisation- data mapper.
World
GDP/capita in ppp terms, (IMF Data Mapper)
1980 - 2010 + forcasts to 2015, showing an apparently increasing
divergence between the 'advanced' and 'emerging and developing'
economies - note the capacity to alter the countries and the
scales of these graphs, and also the plots. Is Germany richer in terms
of GDP/hd than the UK? Was it? How come?
Homework:
See if you can discover what has happened
to GDP (real
terms) per unit of energy use
(i.e. the efficiency of energy use) for the major players -
Canada, China, Russia, India, Brazil, US, Germany, UK, Australia,
Nigeria, South Africa - over the last forty years or so. What do
you conclude?
INCIDENTAL AND CONTEXTUAL INFORMATION
AND DATA RELEVANT TO THE FOOD SECURITY ISSUE.
UNCTAD
- United
Nations Conference on Trade and Development, especially their Foreign
Direct Investment Database (FDI), which presents
aggregate
inflows, outflows, inward stocks and outward stocks of foreign direct
investment (FDI) for 196 reporting economies in an interactive format.
Also produces the World
Investment Report (WIR).
Detailed statistics on foreign direct investment (FDI) and operations
of transnational corporations (TNCs) in selected countries are
available at the World
Investment Directory on-line, which includes country fact
sheets
and profiles.
WTO:
statistical information on:
- Trade Profiles provide predefined information leaflets
on the trade situation of members, observers and other selected
economies;
- Tariff Profiles provide information on the market
access situation of members, observers and other selected economies;
- Services Profiles provide detailed statistics on key
infrastructure services (transportation, telecommunications, finance
and insurance) for selected economies;
- Time Series section allows an interactive data
retrieval of international trade statistics.
See, also, the WTO's new page on Food
Security (November, 2011).
OECD
- basic data for each and all OECD countries (not for emerging or
developing countries).
See, especially, Perspectives
on Global Development 2010: Shifting Wealth: the first
edition of Perspectives on Global Development, a new publication from
the OECD Development Centre: "Shifting Wealth examines the changing
dynamics of the global economy over the last 20 years, and in
particular the impact of the economic rise of large developing
countries, such as China and India, on the poor. It details new
patterns in assets and flows within the global economy and highlights
the strengthening of “South-South” links – the increasing interactions
between developing countries through trade, aid and foreign direct
investment. What do these changes imply for development and
development policy? The report explores potential policy responses at
both national and international levels. Nationally, developing
countries' need to re-position their development strategies to
capitalise on the increasing potential of South-South co-operation and
to fully benefit from new macroeconomic drivers. Internationally, the
global governance architecture needs to adjust to better reflect
current economic weights." [You can
browse this volume, in read only form, from the University Library
e-book section - go and find it].
Some Highlights:
- Non OECD countries (developing countries) are projected to
win a majority share of Global GDP within the next 5 years (p24, Fig
0.6)
- More countries now (in the 'noughties') converging with the
affluent, and fewer are struggling or remain poor cf. the 1990s (p 34,
Figs. 1.5 & 1.6) - note that Brazil still labled here as
'struggling', but see Appendix.
- per capital GDP growth rates (% terms)) converging over the
2000s decade, after diverging during the 90s. (page 38, Fig 1.7) - the
90s a 'lost/disappointing' decade.
- public (government) debt as % of GDP climbing since 1990 in
advanced economies, and both lower and falling in developing and
emerging countries (p62, fig 2.8)
- Poverty rates (% popn. on <$1.25/day) falling in
developing world (even excluding China), from >40% in 1990 to
<30% in 2005 (p99, Fig, 4.1)
- Strong relationship between declining poverty rates and
economic growth (p 99, Fig. 4.2) BUT with much 'unexplained' variation.
International
Labour Organisation: one of whom's major themes is
Globalisation (alongside Sustainability, Poverty, Gender and Aid) -
see, especially, their database of labour statistics,
including international labour migration stats (which tend to be
incomplete).
International
Institute for Environment and Development (IIED) - "an
independent international research organisation, we are specialists in
linking local to global. .. launched in 1971 by renowned economist and
policy advisor Barbara Ward, making it one of the very first
organisations to link environment with development. The institute has
played key roles in the Stockholm Conference of 1972, the Brundtland
Commission of 1987, the 1992 Earth Summit and the 2002 World Summit on
Sustainable Development, and is now helping to shape the global debate
on climate change."
BBSRC (UK)'s Food Security Site.
New England Complex Systems Institute: Food Briefing
ADDITIONAL RELEVANT INFORMATION SITES:
World
Public Opinion: "The WorldPublicOpinion.org website
provides information and analysis about public opinion on international
policy issues from around the world. While the studies of the
WorldPublicOpinion.org network figure prominently, the website draws
together data from a wide variety of sources from around the world. We
have found that data from all reliable sources are important
contributions and that as more studies are integrated into analyses,
world public opinion comes into increasing focus." See, for
example, their recent report of a BBC poll on what opinion is on free
market capitalism.
UNU-Wider:
United Nations University, World Institute for Development Research,
which also has the World
Income
Inequality Database. Country information sheets
provide information about the sources and the surveys used as far as
documentation was available. Country information sheets are only
available in pdf format. The dataset is downloadable as an xl file.
World Economic Forum: (the organisor of the annual Davos
Conference), produces the annual Global
Competitiveness Report, from its Centre for Global Competitiveness
and Performance, (The rankings are calculated from both publicly
available data and the Executive Opinion Survey, a comprehensive annual
survey conducted by the World Economic Forum together with its network
of Partner Institutes (leading research institutes and business
organizations) in the countries covered by the Report). WEF also has a
Corporate Global Citizenship initiative. See the previous page for a complete
listing of the indicators used to compile their Global Competitiveness Index.
Encyclopedia of
Earth: "an electronic reference about the Earth, its natural
environments, and their interaction with society. The Encyclopedia is a
free, fully searchable collection of articles written by scholars,
professionals, educators, and experts who collaborate and review each
other's work. The articles are written in non-technical language and
are useful to students, educators, scholars, professionals, as well as
to the general public."
Council
on Foreign Relations (CFR) [Publisher of Foreign Affairs] has a recent
(19.09.2009) comprehensive report on World
Opinion on the Global Economy. "International polls find strong
support for globalization, though views lean moderately toward the
position that the pace of globalization is too fast. People generally
see international trade as positive for their country, their self and
family, consumers, and their nation’s companies. However, views are
more mixed about the impact of international trade on jobs and the
environment. Polling conducted in the spring of 2009—during the depths
of the global recession—found some softening of majority support for
globalization in general with majorities in many nations favoring a
temporary increase in protectionism in light of the recession.".
CIESIN "The
Center for International Earth Science Information Network (CIESIN) is
a center within the Earth Institute at Columbia University. CIESIN
works at the intersection of the social, natural, and information
sciences, and specializes in on-line data and information management,
spatial data integration and training, and interdisciplinary research
related to human interactions in the environment. See, especially, Thematic
Guide on Political Institutions and Global Environmental Change,
key documents and data sets pertaining to the relationship between
political institutions and the human dimension of global environmental
change. This guide provides only an overview of available information.
GDAE
(pronounced gee-day) Global Development and Environment Institute at
Tufts University. "In our effort to understand actual and possible
trajectories of economic development, GDAE researchers emphasize
ecological health and the correlation between social and economic
well-being. This requires expanding our theoretical understanding of
economic systems, recognizing that they are embedded in the physical
contexts of technology and the natural world, as well as in the
social/psychological contexts of history, politics, ethics, culture,
institutions, and human motivations. Throughout all of its activities,
theoretical advances at GDAE are informed by the Institute's applied
and policy work, while its practical applications of economics are
enhanced by a growing theoretical understanding of what is required to
promote socially and environmentally just and sustainable
development." GDAE is one of three institutions running the Triple Crisis Blog
: “The world is experiencing three
simultaneous crises in finance, development, and the environment.
A number of economists are questioning the mainstream narratives and
analyses of these crises. Some of us have joined to create Triple
Crisis blog to contribute to a more open and global dialogue around
these three crises: about how they interact, and how they can
collectively be solved.”
Global
Dashboard Notes from the future: "Global Dashboard explores
global risks and international affairs, bringing together authors who
work on foreign policy in think tanks, government, academia and the
media. It was set up in 2007 and is edited from the UK by Alex Evans
and David Steven".
BreathingEarth:
Population growth and CO2 emissions starkly and vividly portrayed
(though with no easy access to the underlying data) (link supplied by a member of the 2010
class - thanks.)
Comments and Questions?
Back to DRH index page.


